Kingdoms
of Southeast Asia and Korea
In Southeast Asia’s
river valleys and deltas and on its islands, many kingdoms had centuries of
glory and left monuments of lasting beauty.
Geography of
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia lies
between the Indian and Pacific oceans and stretches from Asia almost to
Australia. It consists of two main parts: (1) Indochina, the mainland
peninsula that borders China to the north and India to the west, and (2) the
islands, the largest of which include Sumatra, Borneo, and Java. All of
Southeast Asia lies within the warm, humid tropics. Monsoon winds bring the
region heavy seasonal rains.
Seas and straits
separate the islands of Southeast Asia. On the mainland, five great rivers
flow from the north and cut valleys to the sea. Between the valleys rise
hills and mountains, making travel and communication difficult. Over time, many
different peoples settled the region, so it was home to many cultures.
Throughout Southeast Asia’s
history, the key to political power often has been control of trade routes
and harbors. This is because Southeast Asia lies on the most direct sea route
between the Indian Ocean and the South China Sea. Two important waterways
connect the two seas: the Strait of Malacca, between the Malay Peninsula and
Sumatra, and the Sunda Strait, between Sumatra and Java.
Influence of India
and China
Indian merchant
ships, taking advantage of the monsoon winds, began arriving in Southeast
Asia by the first century A.D. In the period that followed, Hindu and
Buddhist missionaries spread their faiths to the region. In time, kingdoms
arose that followed these religions and were modeled on Indian political
ideas. Gradually, Indian influence shaped many aspects of the region’s
culture. This early Indian influence on Southeast Asia is evident today in the
region’s religions, languages, and art forms.
Chinese ideas and
culture spread southward in the region through migration and trade. At
different times, the Chinese also exerted political influence over parts of mainland
Southeast Asia, either through direct rule or by demanding tribute from local
rulers.
|
อาณาจักรในเอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงใต้และเกาหลี
ในลุ่มแม่น้ำและสามเหลี่ยมปากแม่น้ำทางเอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงใต้ตลอดจนหมู่เกาะ
อาณาจักรมากมายหลายแห่งมีหลายประเทศที่มีความเจริญรุ่งเรืองและทิ้งอนุสรณ์แห่งความสวยงามหลงเหลือเอาไว้
ภูมิศาสตร์ของเอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงใต้
เอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงใต้ตั้งอยู่ระหว่างอินเดียกับมหาสมุทรแปซิฟิกและทอดยาวเหยียดจากทวีปเอเชียเกือบถึงทวีปออสเตรียเลีย
ประกอบด้วยส่วนหลัก 2 ส่วน คือ (1) อินโดจีน คือ คาบสมุทรที่เป็นแผ่นดินใหญ่มีขอบเขตตั้งแต่จีนทางทิศเหนือและอินเดียทางทิศตะวันตก
และ (2) หมู่เกาะ ที่ใหญ่ที่สุด ประกอบด้วย เกาะสุมาตรา เกาะบอร์เนียว
และเกาะชวา เอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงใต้ทั้งหมดตั้งอยู่ในเขตร้อนชื้น ลมมรสุมพัดพาฝนตามฤดูมาสู่ภูมิภาคนี้
ทะเลและช่องแคบแยกหมู่เกาะออกจากแผ่นดินใหญ่เอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงใต้
บนแผ่นดินใหญ่ แม่น้ำสายใหญ่ 5 สาย ไหลจากทิศเหนือและตัดผ่านหุบเขาลำธารลงไปสู่ทะเล
เกิดเป็นเนินเขาและเทือกเขาระหว่างลุ่มแม่น้ำลำธาร ทำให้การสัญจรและการขนส่งไปมาลำบาก
เมื่อเวลาผ่านไป เกิดมีผู้คนต่าง ๆ มาตั้งหลักแหล่งยังภูมิภาคนั้น
จึงเป็นบ่อเกิดแหล่งวัฒนธรรมมากมาย
ตลอดประวัติศาสตร์เอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงใต้
ปัจจัยหลักสำคัญที่ทำให้ขึ้นสู่อำนาจทางการเมืองอยู่เป็นประจำก็คือการได้เข้าควบคุมเส้นทางการค้าขายและท่าเรือ
ข้อนี้เป็นเพราะเอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงใต้ตั้งอยู่บนเส้นทางทะเลในทิศทางที่ตรงที่สุดระหว่างมหาสมุทรอินเดียกับทะเลจีนใต้
เส้นทางน้ำที่สำคัญ 2 สาย เชื่อมต่อกับทะเลสองแห่ง คือ ช่องแคบมะละกา อยู่ระหว่างคาบสมุทรมาเลย์กับเกาะสุมาตรา
และช่องแคบซุนดา อยู่ระหว่างเกาะสุมาตราและเกาะชวา
อิทธิพลของอินเดียและจีน
เรือของพ่อค้าชาวอินเดีย
ได้เปรียบทางด้านลมมรสุม เริ่มเดินทางเข้ามายังเอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงใต้
ประมาณคริสต์ศตวรรษที่หนึ่ง ในยุคต่อมา
คณะศาสนทูตฮินดูและพุทธศาสนาได้แผ่ขยายคำสอนมายังภูมิภาคนี้ ในไม่ช้า
ราชอาณาจักรทั้งหลายก็ดำเนินตามแบบภูมิภาคนี้และเอาแนวความคิดทางการเมืองของอินเดียเป็นแบบอย่าง
อิทธิพลของอินเดียก็ก่อรูปร่างเป็นลักษณะของวัฒนธรรมประจำภูมิภาคเป็นจำนวนมากมาย
อิทธิพลของอินเดียที่มีต่อเอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงใต้ยุคแรกนี้ยังปรากฏหลักฐานอยู่ในศาสนา
ภาษา และรูปแบบศิลปะประจำภูมิภาคนี้จนทุกวันนี้
แนวความคิดและวัฒนธรรมของจีนได้เผยแผ่ลงมาทางใต้ในภูมิภาคนี้ผ่านการโยกย้ายและการค้าขาย
ณ ช่วงเวลาต่าง ๆ ชาวจีนยังได้ใช้อิทธิพลทางการเมืองเข้าครอบคลุมส่วนต่าง
ๆ ของแผ่นดินใหญ่เอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงใต้ ไม่ผ่านทางการปกครองโดยตรงก็ด้วยการเรียกร้องเครื่องบรรณาการจากเหล่าผู้ปกครองในท้องถิ่น
|
The Khmer Empire
The Khmer (kmair)
Empire, in what is now Cambodia, was for centuries the main power on
the Southeast Asian mainland. By the 800s, the Khmer had conquered
neighboring kingdoms and created an empire. This empire reached the peak of
its power around 1200.
Improved rice
cultivation helped the Khmer become prosperous. The Khmer built elaborate
irrigation systems and waterways. These advances made it possible to grow three
or four crops of rice a year in an area that had previously produced only
one.
At their capital, Angkor, Khmer
rulers built extensive city-and-temple
complexes. One of these, called Angkor Wat, is
one of the world’s greatest architectural achievements. The complex, which covers nearly a square mile, was built as
a symbolic mountain dedicated to the Hindu god Vishnu. The
Khmer also used it as an observatory.
Island Trading
Kingdoms
Powerful kingdoms
also developed on Southeast Asia’s islands.
For example, a dynasty called Sailendra ruled an agricultural kingdom
on the island of Java. The Sailendra kings left behind
another of the world’s great architectural monuments,
the Buddhist temple at Borobudur. Built around 800, this
temple—like Angkor Wat—reflects
strong Indian influence. The massive complex has nine
terraced levels like a stepped pyramid.
The Sailendra Dynasty
eventually fell under the domination of the powerful island empire of
Srivijaya. At its height from the 7th to the 13th
centuries, Srivijaya ruled the Strait of Malacca and other waters around the
islands of Sumatra, Borneo, and Java. It grew wealthy by
taxing the trade that passed through its waters. The Srivijayas established their capital, Palembang, on Sumatra. Palembang became a great center of Buddhist learning, where
Chinese monks could study instead of traveling to India.
|
อาณาจักรเขมร
อาณาจักรเขมร
(แขมร์) ซึ่งปัจจุบันเรียกว่า กัมพูชา มีอิทธิพลสำคัญต่อแผ่นดินใหญ่เอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงใต้เป็นเวลาหลายศตวรรษ
ประมาณศตวรรษที่ 800 เขมรพิชิตอาณาจักรเพื่อนบ้านและสร้างจักรวรรดิขึ้น
จักรวรรดินี้ขึ้นถึงจุดอำนาจสูงสุด ประมาณ 1200 ปี
การเพาะปลูกข้าวที่ได้รับการปรับปรุงให้ดีขึ้นช่วยให้เขมรมีความเจริญรุ่งเรือง
เขมรได้สร้างระบบชลประทานและเส้นทางน้ำที่ซับซ้อน
ความก้าวหน้าเหล่านี้ทำให้สามารถปลูกข้าวได้ 3 หรือ 4 ครั้งต่อปีในพื้นที่ที่เคยผลิตได้เพียงครั้งเดียวเท่านั้น
ณ เมืองหลวง คือ เมืองพระนคร
ผู้ปกครองชาวเขมรได้สร้างเมืองและวิหาร (นครวัด) ที่กว้างขวาง
หนึ่งในนั้นคือนครวัดเป็นหนึ่งในความสำเร็จทางสถาปัตยกรรมที่ยิ่งใหญ่ที่สุดในโลก
ความสลับซับซ้อนซึ่งครอบคลุมเกือบหนึ่งตารางไมล์ถูกสร้างขึ้นเป็นสัญลักษณ์ภูเขา
(พระสุเมรุ) ที่อุทิศให้กับวิษณุ (พระนารายณ์) เทพเจ้าของศาสนาฮินดู นอกจากนี้ ชาวเขมรยังใช้เป็นหอสังเกตการณ์อีกด้วย
อาณาจักรทำการค้าขายกับชาวเกาะ
อาณาจักรที่ทรงอำนาจยังได้พัฒนาหมู่เกาะต่าง
ๆ ของเอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงใต้ให้เจริญรุ่งเรือง ตัวอย่างเช่น ราชวงศ์ที่ไศเลนทร์ ได้ปกครองอาณาจักรเกษตรกรรมบนเกาะชวา
กษัตริย์ไศเลนทร์ ได้ทิ้งร่องรอยอนุสาวรีย์สถาปัตยกรรมที่ยิ่งใหญ่ที่สุดในโลกอีกแห่งหนึ่งซึ่งเป็นวัดทางพุทธศาสนาที่โบโรบูดูร์
(Borobudur)
สร้างขึ้นเมื่อประมาณ ค.ศ. 800 (พ.ศ. 1343) วัดแห่งนี้มีลักษณะคล้ายกับนครวัดซึ่งสะท้อนถึงอิทธิพลของอินเดียที่แข็งแกร่ง
ความสลับซับซ้อนใหญ่โตมหึมามีชั้นเป็นระเบียง 9 ชั้น คล้ายพีระมิดเป็นชั้น ๆ
ในที่สุดราชวงศ์ไศเลนทร์
ก็ตกอยู่ภายใต้การปกครองของจักรวรรดิที่เป็นเกาะที่มีอิทธิพลนามว่าศรีวิชัย
ศรีวิชัยได้ปกครองช่องแคบมะละกาและน่านน้ำอื่น ๆ บริเวณเกาะสุมาตรา บอร์เนียว และชวา
รุ่งเรืองถึงจุดสูงสุด ตั้งแต่คริสต์ศตวรรษที่ 7 ถึง 13 มีความมั่งคั่งด้วยการเก็บภาษีการค้าขายที่ผ่านน้ำ ศรีวิชัยได้ก่อตั้งเมืองหลวง
ชื่อ ปาเล็มบัง ขึ้นบนเกาะสุมาตรา
ปาเล็มบังกลายเป็นศูนย์กลางของการเรียนรู้ทางพุทธศาสนาที่ยิ่งใหญ่ซึ่งเป็นสถานที่ที่พระภิกษุจีนสามารถมาศึกษาได้แทนที่จะเดินทางไปไปยังอินเดีย
|
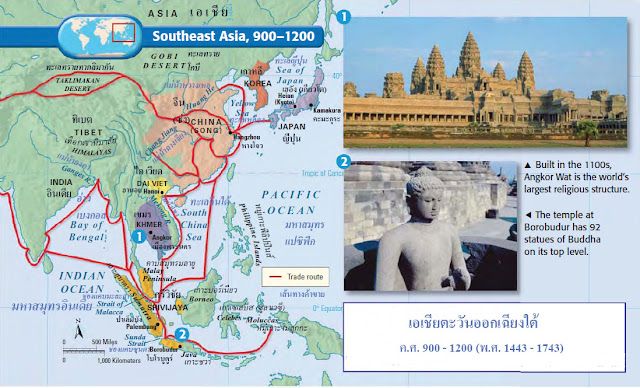 |
1. นครวัด สร้างในคริสต์ศตวรรษที่ 1100 เป็นศาสนสถานที่ใหญ่ที่สุดในโลก
2. วัดโบโรบูดูร์หรือคนไทยเรียกว่าบุโรพุทโธ มีพระพุทธรูป 92 องค์ บนยอดเจดีย์
|
Dai Viet
The people of
Southeast Asia least influenced by India were the Vietnamese. Located
in the coastal region just south of China, Vietnam fell under Chinese
domination. Around 100 B.C., during the mighty Han Dynasty, China took northern Vietnam. When China’s Tang Dynasty weakened in
the early A.D. 900s, Vietnam
managed to break away. It became an independent kingdom,
known as Dai Viet, in 939.
The Vietnamese
absorbed many Chinese cultural influences, including Buddhism and ideas about
government. However, they also preserved a strong spirit
of independence and kept their own cultural identity. Vietnamese
women, for example, traditionally had more freedom and influence than their
Chinese counterparts.
Rulers of the Ly Dynasty (1009–1225) located
their capital at Hanoi, on the Red River delta. They
established a strong central government, encouraged agriculture and trade,
and greatly improved road and river transportation. The
changes made by the Ly continued to influence life in Vietnam long after they
fell from power.
|
อาณาจักรไดเวียด
ผู้คนในเอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงใต้ที่ได้รับอิทธิพลจากประเทศอินเดียน้อยที่สุดคือชาวเวียดนาม
เวียดนามตั้งอยู่ในพื้นที่ชายฝั่งตอนใต้ของจีนเวียดนามตกอยู่ภายใต้การปกครองของจีน
ประมาณ 100 ปีก่อนคริสตกาล ในช่วงราชวงศ์ฮั่นอันยิ่งใหญ่จีนเข้ายึดเวียดนามตอนเหนือ
เมื่อราชวงศ์ถังของจีนเริ่มอ่อนแอลงในช่วงต้นคริสต์ศตวรรษที่ 900 เวียดนามก็ล่มสลายลง
กลายเป็นอาณาจักรอิสระที่รู้จักกันในชื่อ ไดเวียด ในปี ค.ศ. 939 (พ.ศ. 2482)
ชาวเวียดนามได้รับอิทธิพลจากอิทธิพลทางวัฒนธรรมของจีนมากมายรวมถึงพุทธศาสนาและความคิดเกี่ยวกับการปกครอง
อย่างไรก็ตามพวกเขายังคงรักษาจิตวิญญาณแห่งความเป็นอิสระที่เข้มแข็งและคงไว้ซึ่งเอกลักษณ์ทางวัฒนธรรมของตนเอง
ยกตัวอย่างเช่น สตรีชาวเวียดนามยังมีเสรีภาพและมีอิทธิพลตามวัฒนธรรมแบบเดิมมากกว่าสตรีชาวจีน
ผู้ปกครองของราชวงศ์ลี้
(ค.ศ. 1009-1225
= พ.ศ. 1552 - 2768) ตั้งเมืองหลวงขึ้นที่กรุงฮานอยในเขตบริเวณสามเหลี่ยมปากแม่น้ำแดง
พวกเขาจัดตั้งรัฐบาลกลางที่แข็งแกร่ง สนับสนุนการเกษตรและการค้าและการปรับปรุงถนนและการขนส่งทางน้ำอย่างยิ่งใหญ่
การเปลี่ยนแปลงที่เกิดขึ้นโดยราชวงศ์ลี้ยังคงมีอิทธิพลต่อชีวิตในเวียดนามเป็นเวลานานหลังจากที่ราชวงศ์นี้ล่มสลายลงจากอำนาจ
|
Korean Dynasties
According to a Korean
legend, the first Korean state was founded by the hero Tan’gun, whose father
was a god and whose mother was a bear. Another legend relates that it was founded
by a royal descendant of the Chinese Shang Dynasty. These legends reflect two
sides of Korean culture. On one hand, the Koreans were a distinct people who
developed their own native traditions. On the other hand, their culture was shaped
by Chinese influences from early dynastic times. However, like the Japanese,
the Koreans adapted borrowed culture to fit their own needs and maintained a
distinct way of life.
Geography of Korea
Korea is located on a
peninsula that juts out from the Asian mainland toward Japan. It is about the
same size as the state of Utah. Korea’s climate is hot in the summer and very
cold in the winter. Like Japan, Korea is a mountainous land, and only a
limited portion of the peninsula can be farmed. A mountainous barrier lies
between Korea and its northern neighbor, Manchuria. Because of the mountains
and the seas, Korea developed somewhat in isolation from its neighbors.
Early History
In early Korea, as in
early Japan, different clans or tribes controlled different parts of the
country. In 108 B.C., the Han empire conquered much of Korea and established
a military government there. Through the Chinese, Koreans learned about such
ideas as centralized government, Confucianism, Buddhism, and writing. During
Han rule, the various Korean tribes began to gather together into
federations. Eventually, these federations developed into three rival
kingdoms. In the mid-600s, one of these kingdoms, the Silla, defeated the
other kingdoms, drove out the Chinese, and gained control of the whole Korean
peninsula.
Under Silla rule, the
Koreans built Buddhist monasteries and produced elegant stone and bronze
sculptures. They also developed a writing system suitable for writing Korean
phonetically though still using Chinese characters.
|
ราชวงศ์ของเกาหลี
ตามตำนานของเกาหลี
รัฐแห่งแรกของเกาหลีก่อตั้งโดยวีรบุรุษนามว่า ทันกุน ซึ่งมีบิดาเป็นเทพเจ้าและมารดาเป็นหมี
ตำนานอีกแห่งหนึ่งเล่าไว้ว่า ก่อตั้งขึ้นโดยรัชทายาทของราชชางของจีน ตำนานเหล่านี้สะท้อนให้เห็นวัฒนธรรมสองด้านของเกาหลี
อีกด้านหนึ่ง ชาวเกาหลีเป็นผู้ที่พัฒนาวัฒนธรรมของชาติเป็นของตนเองอย่างเด่นชัด ในทางกลับกัน
วัฒนธรรมของเกาหลีก่อเป็นรูปเป็นร่างมาจากอิทธิพลของจีนนับตั้งแต่เริ่มต้นยุคราชวงศ์
แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม ชาวเกาหลีก็คล้ายกับชาวญี่ปุ่นได้รับเอาวัฒนธรรมมาปรับให้เหมาะกับความจำเป็นของตนเองและรักษาวิถีชีวิตไว้อย่างเด่นชัด
ภูมิศาสตร์ของเกาหลี
เกาหลีตั้งอยู่บนคาบสมุทรที่ยื่นออกจากแผ่นดินใหญ่ของเอเชียไปทางญี่ปุ่น
มีขนาดประมาณเท่ากับรัฐยูทาห์ของสหรัฐอเมริกา สภาพภูมิอากาศของเกาหลีจะร้อนในฤดูร้อนและหนาจัดในฤดูหนาว
เกาหลีเป็นประเทศที่เป็นภูเขาและยังมีพื้นที่คาบสมุทรที่สามารถทำเกษตรกรรมได้จำกัด
แนวเขตแดนเทือกเขาทอดไประหว่างเกาหลีและประเทศเพื่อนด้านทิศเหนือ คือ แมนจูเรีย
เนื่องจากเป็นภูเขาและทะเล เกาหลีจึงพัฒนาพื้นที่บางส่วนแยกออกจากเพื่อนบ้าน
ประวัติศาสตร์ยุคแรก
ในประเทศเกาหลีคล้ายกับประเทศญี่ปุ่น
มีเผ่าพงศ์วงศ์วานเข้าครอบครองส่วนต่าง ๆ ของประเทศ เมื่อ 108 ปีก่อนคริสตกาล
จักรวรรดิฮันพิชิตเกาหลีเป็นส่วนมากและสถาปนารัฐบาลทหารขึ้น ณ ที่นั่น ชาวเกาหลีได้เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับแนวความคิด
เช่น มีรัฐบาลเป็นจุดศูนย์กลาง ลัทธิขงจื๊อ พุทธศาสนา และการเขียนมาจากชาวจีน ในช่วงราชวงศ์ฮั่น
เผ่าพันธุ์เกาหลีหลากหลายเริ่มรวมกันเป็นสมาพันธรัฐ ในที่สุด
สมาพันธรัฐเหล่านี้ได้วิวัฒนาการเป็นอาณาจักรที่เป็นศัตรูกัน 3 อาณาจักร เมื่อกลางคริสต์ศตวรรษที่
600 ในบรรดาอาณาจักรเหล่านี้ มีอาณาจักรหนึ่ง นามว่า ซิลลา มีชัยชนะเหนืออาณาจักรอื่น
ๆ ขับไล่ออกไปยังจีน และเข้ายึดครองคาบสมุทรเกาหลีทั้งหมด
ภายใต้การปกครองของอาณาจักรซิลลา
ชาวเกาหลีได้สร้างวัดทางพระพุทธศาสนาและได้ผลิตประมากรรมแกะสลักจากหินและสัมฤทธิ์อันสวยสดงดงาม
ทั้งยังพัฒนาระบบการเขียนให้เหมาะกับการเขียนตามเสียงภาษาเกาหลีแม้จะใช้อักษรจีนอยู่ก็ตาม
|
 | ||
|
The Koryu Dynasty
By the tenth century,
Silla rule had weakened. Around 935, a rebel officer named Wang Kon gained
control of the country and became king. He named his new dynasty Koryu. The Koryu
Dynasty lasted four and a half centuries, from 935 to 1392.
The Koryu Dynasty
modeled its central government after China’s. It also established a civil
service system. However, this system did not provide the social mobility for
Koreans that it did for the Chinese. Koryu society was sharply divided between
a landed aristocracy and the rest of the population, including the military,
commoners, and slaves. Despite the examination system, the sons of nobles
received the best positions, and these positions became hereditary.
The Koryu Dynasty faced a major
threat in 1231, when the Mongols swept into Korea. They demanded a crushing
tribute including 20,000 horses, clothing for 1 million soldiers, and many
children and artisans, who were to be taken away as slaves. The harsh period
of Mongol occupation lasted until the 1360s, when the Mongol Empire
collapsed.
In 1392, a group of
scholar-officials and military leaders overthrew the Koryu Dynasty and
instituted land reforms. They established a new dynasty, called the Choson
(or Yi) Dynasty, which would rule for 518 years.
Koryu Culture
The Koryu period
produced great achievements in Korean culture. Inspired by Song porcelain
artists, Korean potters produced the much-admired celadon pottery, famous for
its milky green glaze. Korean artisans produced one of the great treasures of
the Buddhist world—many thousands of large wooden blocks for printing all the
Buddhist scriptures. This set of blocks was destroyed by the Mongols, but the
disaster sparked a national effort to recreate them. The more than 80,000
blocks in the new set remain in Korea today.
|
อาณาจักรโคริว
ประมาณศตวรรษที่
10 การปกครองของอาณาจักรซิลลาอ่อนแอลง ประมาณ ค.ศ. 935 (พ.ศ. 1478) นายทหารผู้ก่อการกบฏ
นามว่า วัง กอน เข้าควบคุมประเทศและตั้งตัวเป็นกษัตริย์ พระองค์ทรงตั้งราชวงศ์ใหม่ว่า
โคริว ราชวงศ์โคริว ดำรงอยู่ 4
ศตวรรษครึ่ง ตั้งแต่ ค.ศ. 935 ถึง ค.ศ. 1392 (พ.ศ. 1478 – 1935)
ราชวงศ์โคริวจำลองแบบการปกครองแบบมีจุดศูนย์กลางตามจีน
ทั้งยังสถาปนาระบบราชการพลเรือน แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม
ระบบนี้ไม่ได้ทำให้เกิดการเปลี่ยนแปลงทางสังคมให้กับเกาหลีได้รวดเร็วเหมือนกับจีน
สังคมโคริวถูกแบ่งอย่างเข้มงวดระหว่างขุนนางที่เป็นเจ้าของที่ดินและประชากรอื่น
ๆ ประกอบด้วยทหาร สามัญชน และเหล่าทาส แม้จะมีระบบการสอบแข่งขัน
บุตรของขุนนางก็ได้รับตำแหน่งที่ดีที่สุดและตำแหน่งเหล่านี้ก็กลายมรดกตกทอด
ราชวงศ์โคริวเผชิญกับการคุกคามครั้งใหญ่ในปี
ค.ศ. 1231 (พ.ศ. 1774) เมื่อชาวมองโกลแผ่อำนาจเข้าสู่เกาหลี พวกมองโกลต้องการเครื่องบรรณาการแบบเด็ดขาด
ประกอบด้วย ม้า 20,000 ตัว เครื่องนุ่งห่มสำหรับทหาร 1 ล้านคน และเด็ก ๆ
ตลอดจนช่างฝีมือจำนวนมากเพื่อเอาไปเป็นทาส ช่วงเวลาที่ทุกข์ยากลำบากจากการที่พวกมองโกลยึดครองดำรงอยู่จนถึงทศวรรษที่
1360 เมื่อจักรวรรดิมองโกลล่มสลายลง
ในปี ค.ศ.
1392 (พ.ศ. 1935) ราชบัณฑิตและผู้นำทางทหารได้โค่นล้มราชวงศ์โคริวและจัดการปฏิรูปแผ่นดิน ชนเหล่านั้นได้สถาปนาราชวงศ์ใหม่ เรียกว่า
ราชวงศ์โชซ็อน (หรือ อี) ซึ่งปกครองเป็นเวลา 518 ปี
วัฒนธรรมโคริว
ยุคโคริวได้สร้างความสำเร็จอย่างยิ่งใหญ่ให้กับวัฒนธรรมเกาหลี
ช่างปั้นชาวเกาหลีซึ่งได้รับแรงบันดาลใจจากศิลปินเครื่องลายครามแห่งราชวงศ์ซ่งได้ผลิตเครื่องปั้นดินเผาที่ทำจากศิลาดลที่ได้รับการยกย่องเป็นอย่างมาก
ที่มีชื่อเสียงให้กับเครื่องเคลือบสีเขียวอ่อน ช่างฝีมือชาวเกาหลีได้สร้างขุมสมบัติอันยิ่งใหญ่แห่งหนึ่งของโลกพระพุทธศาสนา
คือ ชิ้นไม้ขนาดใหญ่หลายพันชิ้นที่ใช้พิมพ์พระไตรปิฎกทั้งหมด ชิ้นไม้เหล่านี้ถูกทำลายโดยชาวมองโกล
แต่ความหายนะนี้เป็นจุดเริ่มต้นของความพยายามของชาติในการสร้างชิ้นไม้เหล่านั้นขึ้นมาใหม่
พระไตรปิฎกไม้ชุดใหม่มากกว่า 80,000 ชุด ยังคงเหลืออยู่ในเกาหลีในปัจจุบันนี้
|
Haein-sa
Temple
Haein-sa Temple, or the Temple
of Reflection on a Calm Sea, is one of the most important Buddhist centers in
South Korea. According to legend, the temple was built
in the early 800s by a king of Silla. He wanted to honor
the Buddha because two Buddhist monks had cured his wife of a deadly disease.
Haein-sa Temple is best known
as the home of the Tripitaka Koreana, a collection of more than 81,000 wooden
printing blocks dating from the mid-1200s.
They provide the world’s most complete collection
of Buddhist texts.
In recognition of the Tripitaka’s
historical and religious importance, the United Nations Educational, Scientific
and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) named
Haein-sa Temple a world cultural heritage site in 1995.
วัดแฮอินซา
วัดแฮอินซา (Haein-sa Temple) หรือ วัดแห่งการสะท้อนบนทะเลอันเงียบสงบ (Temple of Reflection on Calm Sea) เป็นศูนย์กลางทางพุทธศาสนาที่สำคัญที่สุดแห่งหนึ่งในเกาหลีใต้
ตามตำนานวัดนี้สร้างขึ้นในช่วงต้นศตวรรษที่ 800
โดยกษัตริย์แห่งราชวงศ์ซิลลา พระองค์มีพระประสงค์จะถวายเกียรติแด่พระพุทธเจ้า เพราะมีพระภิกษุสงฆ์จำนวน
2 รูป รักษาพระมเหสีของพระองค์ให้หายจากโรคร้ายแรง
วัดแฮอินซาเป็นที่รู้จักกันดีในฐานะเป็นที่เก็บพระไตรปิฎกเกาหลี
Tripitaka
Koreana?????? ซึ่งเป็นชิ้นไม้แกะสลักพระไตรปิฎกมากกว่า 81,000 ชิ้น ซึ่งมีอายุมาตั้งแต่กลางทศวรรษ 1200
เป็นตำราทางพุทธศาสนาที่สมบูรณ์แบบที่สุดในโลก
องค์การเพื่อการศึกษาวิทยาศาสตร์และวัฒนธรรมแห่งสหประชาชาติ
(UNESCO)
ได้ขึ้นชื่อวัดแฮอินซาเป็นมรดกโลกทางวัฒนธรรมในปี ค.ศ. 1995 (พ.ศ.
2538)
|
|
|
|
Two Koreas
Since the end of
World War II, Korea has been arbitrarily divided into two countries—communist North Korea and democratic South Korea. For years, many Koreans longed for their country to be
reunited.
Hopes for such a day
rose in 2000 when the presidents of the two nations sat down to discuss
reunification. In 2002, however, North Korea announced
that it was developing nuclear weapons and would use them against South Korea
if necessary. This greatly dimmed people’s
hopes for one Korea.
ประเทศเกาหลี 2 ประเทศ
นับตั้งแต่สิ้นสุดสงครามโลกครั้งที่สอง
เกาหลีถูกแบ่งออกเป็น 2 ประเทศโดยพลการ คือ เกาหลีเหนือเป็นคอมมิวนิสต์และเกาหลีใต้เป็นประชาธิปไตย
เป็นเวลาหลายปีมาแล้ว ชาวเกาหลีจำนวนมากปรารถนาให้ประเทศของตนรวมตัวกันใหม่ ความหวังวันดังกล่าวจะเกิดขึ้นในปี
ค.ศ. 2000 (พ.ศ. 2543) ประธานาธิบดีของสองประเทศได้นั่งลงหารือเกี่ยวกับการรวมตัวกันใหม่
แต่อย่างไรก็ตามในปี ค.ศ. 2002 (พ. ศ. 2545) เกาหลีเหนือได้ประกาศว่ากำลังพัฒนาอาวุธนิวเคลียร์และจะใช้อาวุธเหล่านั้นต่อต้านเกาหลีใต้ถ้าจำเป็น
เรื่องนี้ทำให้ความหวังของผู้คนที่จะให้เกาหลีเป็นหนึ่งเดียวเลือนรางลง
|



