The
Geography of Early Nubia
South of Egypt, a group of people
settled in the region we now call Nubia. These Africans
established the fi rst great kingdom in the interior of Africa.
We know this kingdom by the name the Egyptians gave it—Kush. The development of Kushite society was greatly influenced by
the geography of Nubia, especially the role played by the Nile River.
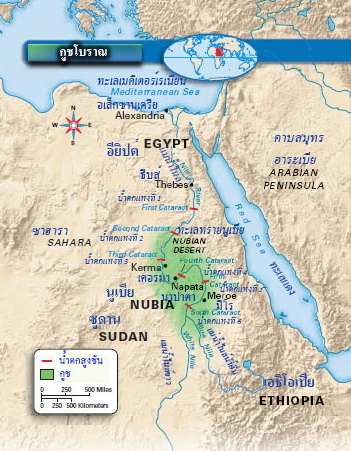
The Land of
Nubia
Today desert covers much of Nubia,
but in ancient times the region was more fertile than it is now.
Rain flooded the Nile every year, providing a rich layer of silt to
nearby lands. The kingdom of Kush developed in this
fertile area.
Ancient Nubia was
rich in minerals such as gold, copper, and stone. These resources
played a major role in the area’s history and
contributed to its wealth.
Early
Civilization in Nubia
Like all early civilizations, the
people of Nubia depended on agriculture for their food. Fortunately
for them, the Nile’s floods
allowed
the Nubians to plant both summer and winter crops.
Among the crops they grew were wheat, barley, and other grains.Besides farmland, the banks of the Nile also provided grazing land for livestock. As a result, farming villages thrived all along the Nile by 3500 BC.
Over time some farmers grew richer than
others. These farmers became village leaders. Sometime around 2000 BC, one of these leaders took control
of other villages and made himself king of the region. His
new kingdom was called Kush.
The kings of Kush ruled from their capital
at Kerma. This city was located on the Nile just south
of the third cataract. Because the Nile’s
cataracts made parts of the river hard to pass through, they were natural
barriers against invaders. For many years the cataracts
kept Kush safe from the more powerful Egyptian kingdom to the north.
As time passed, Kushite society grew
more complex. Besides farmers and herders, some Kushites
became priests and artisans. Early Kush was influenced
by cultures to the south. Later, Egypt played a greater role
in Kush’s history.
|
ภูมิศาสตร์ของนูเบียยุคแรก
ทางตอนใต้ของอียิปต์ มีกลุ่มผู้คนที่ตั้งรกรากในภูมิภาคที่ปัจจุบันนี้เรียกกันว่า
นูเบีย (Nubia) ชาวแอฟกันเหล่านี้ได้ก่อตั้งอาณาจักรแห่งแรกในตอนกลางทวีปแอฟริกา
เรารู้จักอาณาจักรนี้ตามชื่อที่ชาวอียิปต์ตั้งให้ คือ กูช (Kush) วิวัฒนาการของสังคมกูชได้รับอิทธิพลจากภูมิศาสตร์ของนูเบียเป็นอย่างมาก
โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่ง การแสดงบทบาทตามลำแม่น้ำไนล์
แผ่นดินนูเบีย
ปัจจุบันนี้
ทะเลทรายปกคลุมนูเบียเป็นส่วนมาก แต่ในครั้งโบราณ ภูมิภาคนี้อุดมสมบูรณ์มากกว่าปัจจุบันนี้
ฝนไหลหลากท่วมแม่น้ำไนล์ทุก ๆ ปี
เตรียมชั้นโคลนอันอุดมสมบูรณ์ให้กับแผ่นดินบริเวณรอบ ๆ
อาณาจักรกูลพัฒนาในบริเวณอันอุดมสมบูรณ์นี้
นูเบียโบราณอุดมไปด้วยแร่ธาตุมากมาย
เช่น ทองคำ ทองแดง และหิน ทรัพยากรเหล่านี้มีบทบาทสำคัญในประวัติศาสตร์ของบริเวณนี้และสนับสนุนให้เกิดความมั่งคั่ง
อารยธรรมยุคแรกในนูเบีย
เหมือนกับอารยธรรมยุคแรกทั้งหมด
ผู้คนในนูเบียได้อาศัยเกษตรกรรมเป็นอาหาร เป็นความโชคดีสำหรับผู้คนเหล่านั้น
กระแสน้ำหลากแห่งแม่น้ำไนล์ทำให้นูเบียปลูกพืชพันธุ์ได้ทั้งฤดูร้อนและฤดูหนาว ในบรรดาพืชพันธุ์เหล่านั้นที่ผู้คนปลูก
คือ ข้าวสาลี ข้าวบาร์เลย์ และข้าวอื่น ๆ
นอกจากที่ดินทำมาหากินแล้ว
ฝั่งแม่น้ำไนล์ยังให้ทุ่งเลี้ยงสัตว์สำหรับเลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
เป็นผลให้หมู่บ้านเกษตรกรรมมีความเจริญเติบโตทั่วไปตามลำแม่น้ำไนล์ เมื่อประมาณ
3,500 ปีก่อนคริสตกาล
เมื่อเวลาผ่าน
เกษตรกรบางพวกมีความอุดมสมบูรณ์มากกว่าเกษตรกรพวกอื่น ๆ
เกษตรกรเหล่าจึงกลายเป็นผู้นำหมู่บ้าน บางครั้ง ประมาณ 2,000 ปีก่อนคริสตกาล
ผู้นำเหล่านี้คนหนึ่งได้ปกครองหมู่บ้านอื่น ๆ
และสถาปนาตัวเองให้เป็นกษัตริย์แห่งภูมิภาคนี้ ราชอาณาจักรใหม่ของพระองค์
จึงเรียกว่า กูช
กษัตริย์แห่งกูชได้ปกครองตั้งแต่เมืองหลวงที่เคอร์มา
(Kerma) เมืองหลวงนี้ตั้งอยู่บนฝั่งแม่น้ำไนล์
เพียงแค่ลงไปทางใต้น้ำตกสูงชันแห่งที่สาม เนื่องจากน้ำตกสูงชันของแม่น้ำไนล์ให้แม่น้ำไนล์หลายส่วนผ่านไปได้ยาก
น้ำตกสูงชันเหล่านั้นจึงเป็นแนวกั้นเขตทางธรรมชาติต่อผู้รุกราน เป็นเวลาหลายปี
น้ำตกสูงชันเหล่านั้นได้รักษาความปลอดภัยจากราชอาณาจักรอียิปต์ที่มีอำนาจมากกว่าที่อยู่ทางทิศเหนือ
เมื่อเวลาผ่านไป
สังคมกูลก็เจริญสลับซับซ้อนมากขึ้น นอกจากเกษตรกรและคนเลี้ยงปศุสัตว์แล้ว
ชาวกูชบางพวกก็เป็นนักบวชและช่างฝีมือ
กูชในยุคแรกได้รับอิทธิพลจากวัฒนธรรมทางตอนใต้ ต่อมา
อียิปต์จึงมีบทบาทยิ่งใหญ่ขึ้นในประวัติศาสตร์ของกูช
|
Kush
and Egypt
Kush and Egypt were neighbors. Sometimes the neighbors lived in peace with each other and
helped each other prosper. For example, Kush became a
major supplier of both slaves and raw materials to Egypt. The
Kushites sent materials such as gold, copper, and stone to Egypt. The Kushites also sent the Egyptians ebony, a type of dark, heavy
wood, and ivory, the hard white material that makes up elephant tusks.
Egypt’s Conquest of Kush
Relations between Kush and Egypt
were not always peaceful, however. As Kush grew wealthy
from trade, its army grew stronger as well. Egypt’s rulers soon feared that Kush would grow even more powerful and
attack Egypt.
To prevent such an attack from
occurring, the pharaoh Thutmose I sent an army to take control of Kush around
1500 BC. The pharaoh’s army
conquered all of Nubia north of the Fifth Cataract. As a
result, Kush became part of Egypt.
After his army’s
victory, the pharaoh destroyed Kerma, the Kushite capital. Later
pharaohs—including Ramses the Great—built
huge temples in what had been Kushite territory.
|
กูชและอียิปต์
กูชและอียิปต์เป็นเพื่อบ้านกัน
บางครั้ง เพื่อนบ้านก็อยู่ด้วยกันอย่างสันติสุข
ช่วยกันและกันให้เกิดความรุ่งเรือง ยกตัวอย่างเช่น กูชเป็นผู้จัดหาทั้งทาสและวัตถุดิบรายสำคัญให้กับอียิปต์
ชาวกูชได้ส่งวัตถุดิบ เช่น ทองคำ ทองแดงและหินไปยังอียิปต์ และยังได้จัดส่งไม่เนื้อแข็งสีดำและงาช้างไปให้อียิปต์ด้วย
อียิปต์พิชิตกูช
อย่างไรก็ตาม
ความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างกูชกับอียิปต์ไม่ได้อยู่ในสันติภาพเสมอไป
ในขณะที่กูชรุ่งเรืองมั่งคั่งจากการค้าขาย และยังมีกองทัพที่แข็งแกร่งอีกด้วย
ในไม่ช้า ผู้ปกครองชาวอียิปต์ก็กลัวว่า กูชจะมีความเจริญรุ่งเรืองมีอำนาจมากกว่าและจะเข้าโจมตีอียิปต์
เพื่อป้องกันไม่ให้เกิดการโจมตีดังกล่าว
ฟาโรห์ทุตโมสที่ 1 ก็ได้ส่งกองทัพไปยึดกูชประมาณ 1,500 ปีก่อนคริสตกาล
กองทัพของฟาโรห์ได้พิชิตนูเบียที่อยู่ทางตอนเหนือของน้ำตกสูงชันแห่งที่ห้าทั้งหมด
เป็นผลให้กูชตกเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของอียิปต์
หลังจากกองทัพของฟาโรห์ได้รับชัยชนะ
พระองค์ได้ทำหลายเมืองเคอร์มา ที่เป็นเมืองหลวงของกูช
ต่อมาฟาโรห์รวมทั้งรามเสสมหาราชก็ได้สร้างวิหารขนาดมหึมาในดินแดนของกูช
|
Effects of
the Conquest
Kush remained an Egyptian territory
for about 450 years. During that time, Egypt’s influence over Kush grew tremendously. Many
Egyptians settled in Kush. Egyptian became the language
of the region. Many Kushites used Egyptian names and
wore Egyptian-style clothing. They
also adopted Egyptian religious practices.
A Change in
Power
During the mid-1000s
BC the New Kingdom in Egypt was ending. As the power of Egypt’s pharaohs declined, Kushite leaders regained control of Kush. Kush once again became independent.
We know almost nothing about the history
of the Kushites from the time they gained independence until 200 years later. Kush is not mentioned in any historical records that
describe those centuries.
The
Conquest of Egypt
By around 850 BC Kush had regained
its strength. It was once again as strong as it had been
before it had been conquered by Egypt. Because the
Egyptians had captured and destroyed the city of Kerma, the kings of Kush
ruled from the city of Napata. Built by the Egyptians,
Napata was on the Nile, about 100 miles southeast of Kerma.
As Kush grew stronger, Egypt was
further weakened. A series of inept pharaohs left Egypt open to
attack. In the 700s BC a Kushite king, Kashta, seized on
Egypt’s weakness and attacked it. By
about 751 BC he had conquered Upper Egypt. He then established
relations with Lower Egypt.
After Kashta died, his son Piankhi
continued to attack Egypt. The armies of Kush captured
many cities, including Egypt’s ancient capital. Piankhi fought the Egyptians because he believed that the
gods wanted him to rule all of Egypt. By the time he
died in about 716 BC, Piankhi had accomplished this task. His
kingdom extended north from Napata to the Nile Delta.
|
ผลกระทบจากการพิชิต
กูชยังคงเป็นอาณานิคมของอียิปต์
เป็นเวลาประมาณ 450 ปี ในช่วงเวลานั้น
อิทธิพลของอียิปต์ที่มีเหนือกูชก็รุ่งเรืองเต็มที่
ภาษาอียิปต์ก็กลายเป็นภาษาทางการของภูมิภาคนี้
ชาวกูชจำนวนมากได้ใช้ชื่ออียิปต์และสวมเสื้อผ้าสไตล์อียิปต์
และยังยอมรับนับถือศาสนาแบบอียิปต์ด้วย
การเปลี่ยนแปลงอำนาจ
ในช่วงกลางศตวรรษที่
1000 ก่อนคริสตกาล ราชอาณาจักรใหม่ในอียิปต์ก็สิ้นสุดลง
ในขณะที่อำนาจของฟาโรห์อียิปต์สิ้นสุดลง ผู้นำกูชก็ยึดการปกครองกูชคืนมา
กูชก็กลายเป็นเอกราชอีกครั้ง
พวกเราเกือบไม่รู้อะไรเลยเกี่ยวกับประวัติศาสตร์ของกูชนับตั้งแต่เวลาที่ได้รับเอกราชจนถึง
200 ปี ต่อมา กูชไม่ได้รับการกล่าวถึงด้วยการบันทึกทางประวัติศาสตร์ใด ๆ
ในช่วงศตวรรษเหล่านี้เลย
การพิชิตอียิปต์
เมื่อประมาณ
850 ปี ก่อนคริสตกาล กูชได้ฟื้นฟูความแข็งแกร่งกลับคืนมา มีความแข็งแกร่งอีกครั้ง
พอ ๆ กับช่วงเวลาก่อนที่กูชจะถูกอียิปต์พิชิต เนื่องจากชาวอียิปต์ได้ยึดและทำลายเมืองเคอร์มา
กษัตริย์กูชได้ปกครองตั้งแต่เมืองนาปาตา (Napata) เมืองนาปาตาสร้างโดยชาวอียิปต์
อยู่บนฝั่งแม่น้ำไนล์ ประมาณ 100 ไมล์ไปทางใต้ของเมืองเคอร์มา
ในขณะที่กูชมีความเข้มแข็งมากขึ้น
อียิปต์ก็เกิดความอ่อนแออย่างมาก ฟาโรห์ที่ไร้ความสามารถก็ปล่อยให้อียิปต์ถูกโจมตีเป็นระยะ
ๆ เมือศตวรรษที่ 700 ก่อนคริสตกาล กษัตริย์กูชนามว่า กัชตา (Kashta)
ก็ฉกฉวยโอกาสที่อียิปต์อ่อนแอและโจมตีอียิปต์ เมื่อประมาณ 751 ปี ก่อนคริสตกาล
พระองค์ได้พิชิตอียิปต์ตอนบนแล้วก็สถาปนาความสัมพันธ์กับอียิปต์ตอนล่าง
หลังจากกษัตริย์กัชตาสวรรคต
โอรสของพระองค์นามว่า เปียงคี (Piankhi) ก็โจมตีอียิปต์ต่อไป
กองทัพของกูชได้ยึดเมืองของอียิปต์มากมาย รวมทั้งเมืองโบราณ เปียงคี (ไปอันคี,
ปิอันคี – ข้อมูลไม่มีเลย) ได้ต่อสู้กับชาวอียิปต์
เนื่องจากพระองค์เชื่อว่า เทพเจ้าทั้งหลายต้องการให้พระองค์ปกครองอียิปต์ทั้งหมด
ก่อนเวลาที่พระองค์จะสวรรคตเมื่อประมาณ 716 ปีก่อนคริสตกาล
เปียงคีก็ได้ทำภารกิจนี้สำเร็จ
ราชอาณาจักรของพระองค์ขยายไปทางเหนือตั้งแต่เมืองนาปาตาจนถึงสามเหลี่ยมแม่น้ำไนล์
|
The End of
Kushite Rule in Egypt
The Kushite Dynasty remained strong
in Egypt for about 40 years. In the 670s BC, however,
the powerful army of the Assyrians from Mesopotamia invaded Egypt. The Assyrians’ iron weapons were better
than the Kushites’ bronze weapons. Although
the Kushites were skilled archers, they could not stop the invaders. The Kushites were steadily pushed southward. In
just 10 years the Assyrians had driven the Kushite forces completely out of
Egypt.
Later
Kush
After they lost control of Egypt,
the people of Kush devoted themselves to agriculture and trade, hoping to
make their country rich again. Within a few centuries,
the kingdom of Kush had indeed become prosperous and powerful once more.
Kush’s Iron Industry
The economic center of Kush during
this period was at Meroë, the kingdom’s new capital. Meroë’s location on the east bank of
the Nile helped Kush’s economy to grow. Large
deposits of gold could be found nearby, as could forests of ebony and other
wood. More importantly, the area around Meroë was full
of rich iron ore deposits.
In this location, the Kushites
developed Africa’s first iron industry. Iron
ore and wood for furnaces were easily available, so the iron industry grew
quickly.
The
Expansion of Trade
In time, Meroë became the center of
a large trade network, a system of people in different lands who trade
goods. The Kushites sent goods down the Nile to Egypt. From
there,
Egyptian and Greek merchants, or traders, carried goods to
ports on the Mediterranean and Red seas and to southern Africa.
These goods may have eventually reached India, and perhaps China.
Kush’s exports
—items sent out to other regions—included
gold, pottery, iron tools, slaves, and ivory. Kushite
merchants also exported leopard skins, ostrich feathers, and elephants. In return, the Kushites received imports —goods brought in from other regions—such
as fi ne jewelry and luxury items from Egypt, Asia, and other lands along the
Mediterranean Sea.
Kushite Culture
As Kushite trade grew, merchants
came into contact with people from other cultures. As a
result, the people of Kush combined customs from other cultures with their
own unique Kushite culture.
The most obvious influence on
Kushite culture was Egypt. Many buildings in Meroë,
especially temples, resembled those in Egypt. Many
people in Kush worshipped Egyptian gods and wore Egyptian clothing. Kushite rulers used the title pharaoh and were buried
in pyramids.
Many elements of Kushite culture
were not borrowed. Kushite houses and daily life were
unique. One Greek geographer noted some Kushite
differences.
“The houses in the cities
are formed by interweaving split pieces of palm wood or of bricks. . . . They hunt elephants, lions, and panthers.
There are also serpents . . . and there are many
other
kinds of wild animals.”
–Strabo, The Geographies
In addition to Egyptian gods, the
people of Kush worshipped their own gods. They also
developed their own written language, Meroitic. Unfortunately,
historians are not yet able to understand Meroitic.
|
สิ้นสุดการปกครองของกูชในอียิปต์
ราชวงศ์กูชยังคงมีความเข้มแข็งในอียิปต์เป็นเวลาประมาณ
40 ปี อย่างไรก็ตาม เมื่อ ศตวรรษที่ 670 ก่อนคริสตกาล กองทัพอันเกรียงไกรของชาวอัสซีเรีย
จากเมโสโปเตเมียก็เข้ารุกรานอียิปต์
อาวุธเหล็กของอัสซีเรียมีประสิทธิภาพดีกว่าอาวุธสัมฤทธิ์ของกูช แม้ว่ากูชจะมีพลธนูผู้มีทักษะ
พวกเข้าก็สามารถหยุดการรุกรานได้ กูชจึงถูกผลักดันลงไปทางใต้แทน เพียง 10 ปี
ชาวอัสซีเรียก็ขับไล่กองทัพกูชออกจากอียิปต์ได้อย่างสิ้นเชิง
กูชยุคต่อมา
หลักจากพวกกูชสูญเสียการครอบครองอียิปต์
ผู้คนชาวกูชก็ทุ่มเทตนเองให้กับเกษตรกรรมและพาณิชยกรรม ด้วยความหวังที่ทำให้ประเทศของตนเองกลับมาร่ำรวยอีกครั้ง
ภายในสองสามศตวรรษ
ราชอาณาจักรกูชก็รุ่งเรืองและเกรียงไกรมากกว่าเก่าอย่างแท้จริง
อุตสาหกรรมเหล็กของกูช
ศูนย์กลางเศรษฐกิจของกูชในระหว่างเวลานี้อยู่ที่เมืองมีโร
(Meroë) ซึ่งเป็นเมืองหลวงใหม่ของอาณาจักร
ตั้งอยู่บนฝั่งตะวันออกของแม่น้ำไนล์ ช่วยให้เศรษฐกิจของกูชเจริญรุ่งเรือง มีแหล่งทองคำขนาดใหญ่ที่สามารถค้นพบได้บริเวณรอบ
ๆ ป่าไม้เนื้อแข็งสีดำและไม้อื่น ๆ ก็พบได้เช่นกัน ที่สำคัญยิ่งกว่านั้น
บริเวณรอบๆ เมืองมีโรอุดมไปด้วยแหล่งแร่เหล็กมากมาย
ณ ตำแหน่งนี้
ชาวกูชจึงได้พัฒนาอุตสาหกรรมเหล็กเป็นแห่งแรกของแอฟริกา แร่เหล็กและไม้สำหรับเตาหลอม
ก็หาได้ง่าย ดังนั้น อุตสาหกรรมเหล็กจึงเจริญรุดหน้าไปอย่างรวดเร็ว
การขยายการค้าขาย
ในไม่ช้า
เมืองมีโรก็กลายเป็นศูนย์กลางของเครือข่ายการค้าขายขนาดใหญ่
ซึ่งเป็นระบบของผู้คนในดินแดนต่าง ๆ ที่มาค้าขายสินค้า ชาวกูชได้ส่งสินค้าลงไปตามแม่น้ำไนล์ไปยังอียิปต์
จากที่นั้น
เหล่าพ่อค้าชาวอียิปต์และกรีกก็นำสิ้นไปยังท่าเรือบนฝั่งทะเลเมดิเตอร์เรเนียนและทะเลแดง
ตลอดจนนำไปสู่แฟริกาตะวันตก ในที่สุด
สิ้นค้าเหล่านี้ อาจจะไปถึงอินเดียและบางทีไปถึงจีน
สินค้าส่งออกของกูช
ซึ่งส่งออกไปยังภูมิภาคอื่น ๆ ได้แก่ ทองคำ เครื่องปั้นดินเผา เครื่องมือเหล็ก
และงาช้าง เหล่าพ่อค้าชาวกูช ยังได้ส่งหนังเสือดาว ขนนกกระจอกเทศและช้างอีกด้วย ในทางกลับกัน
สินค้านำเข้า ที่กูชนำเข้ามาจากภูมิภาคอื่น ๆ เช่น
เครื่องเพชรพลอยอันสวยงามและสินค้าหรูหราจากอียิปต์ เอเชีย และดินแดนอื่น ๆ
ตามแนวทะเลเมดิเตอร์เรเนียน
วัฒนธรรมกูช
ในขณะที่การค้าขายของกูชเจริญรุ่งเรือง
เหล่าพ่อค้าก็มีการติดต่อสัมพันธ์กับผู้คนจากวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ เป็นผลให้ประชาชนชาวกูชได้เชื่อมสัมพันธ์วัฒนธรรมประเพณีจากวัฒนธรรมอื่น
ๆ เข้ากับวัฒนธรรมกูชอันเป็นเอกลักษณ์ของตนเอง
อิทธิพลที่เด่นชัดมากที่สุดที่มีต่อวัฒนธรรมกูชก็คืออียิปต์
อาคารมากมายในเมืองมีโร โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งในวิหาร มีความคล้ายคลึงกับอียิปต์
ประชาชนส่วนมากในกูชเคารพนับถือเทพเจ้าของอียิปต์และสวมเสื้อผ้าแบบอียิปต์ ผู้ปกครองชาวกูชใช้นามว่า
ฟาโรห์ และพระศพก็ถูกฝังไว้ในพีระมิด
รากฐานของวัฒนธรรมกูชมากมายไม่ได้รับการถ่ายทอด
อาคารและการดำเนินชีวิตประจำวันของชาวกูชมีเอกลักษณ์เฉพาะตัว นักภูมิศาสตร์ชาวกรีกคนหนึ่งได้เขียนบันทึกความแตกต่างของกูชไว้ว่า
“อาคารบ้านช่องในเมืองหลายเมืองสร้างขึ้นจากการผสมผสานชิ้นส่วนของต้นปาล์มหรือก้อนอิฐ...
พวกเขาล่าช้าง สิงโต และเสือดำ
ยังมีงูใหญ่อีกด้วย...และมีสัตว์ชนิดอื่นมากมาย”
--สตราโบ (Strabo), The
Geographies
นอกจาเทพเจ้าของอียิปต์แล้ว
ชาวกูชก็นับถือเทพเจ้าของตนเอง พวกเขายังได้พัฒนาภาษาเขียนเป็นของตนเอง คือ ภาษา
มีโรอิติก (Meroitic) เป็นที่น่าเสียดายที่นักประวัติศาสตร์ยังไม่สามารถเข้าใจภาษามีโรอิติกได้
|
Women in
Kushite Society
The women of Kush were expected to
be active in their society. They worked in the fields,
raised children, cooked, and performed other household tasks.
Some Kushite women rose to positions
of authority. Some served as co-rulers
with their husbands or sons. A few women ruled the
empire alone. Historians believe that the fi rst woman
to rule Kush was Queen Shanakhdakheto. She ruled
from 170 BC to 150 BC.
The
Decline of Kush
Kush gradually declined in power. A series of problems within the kingdom weakened its economy. One problem was that Kush’s cattle were
allowed to overgraze. When cows ate all the grass, wind
blew the soil away, causing farmers to produce less food.
In addition, ironmakers used up the forests
near Meroë. As wood became scarce, furnaces shut down. Kush produced fewer weapons and trade goods.
Kush was also weakened by a loss of
trade. Foreign merchants set up new trade routes that
went around Kush. One such trade route bypassed Kush in
favor of Aksum, a kingdom located along the Red Sea in what is today Ethiopia
and Eritrea. In the fi rst two centuries AD, Aksum grew
wealthy from trade.
By the AD 300s Kush had lost much of
its wealth and military might. The king of Aksum took
advantage of his former trade rival’s weakness. In about AD 350 the Aksumite army of King Ezana destroyed
Meroë and took over Kush.
In the late 300s, the rulers of Aksum became
Christian. About two hundred years later, the Nubians
also converted. The last influences of Kush had
disappeared.
|
สตรีในสังคมกูช
สตรีของกูชได้รับความคาดหวังว่าจะเป็นผู้มีความกระตือรือร้นในสังคม
พวกหล่อนทำงานในทุ่งนา เลี้ยงดูลูก ๆ ทำครัวและทำงานบ้านอื่น ๆ
สตรีชาวกูชบางคนขึ้นสู่ตำแหน่งที่สูงในทางราชการ
บางคนทำงานในฐานะเป็นผู้ช่วยผู้ปกครองร่วมกับสามีและบุตรของตนเอง
สตรีจำนวนเล็กน้อยที่ปกครองจักรวรรดิแต่เพียงผู้เดียว นักประวัติศาสตร์เชื่อว่า
สตรีคนแรกที่ปกครองกูช คือ ราชินี ชานัคดาคีโต (Queen Shanakhdakheto) พระนางปกครองตั้งแต่
170 ถึง 150 ปี ก่อนคริสตกาล
การเสื่อมลงของกูช
กูชได้ค่อย ๆ
สูญสิ้นอำนาจตามลำดับ มีปัญหาภายในราชอาณาจักรมาเป็นระยะ ๆ ทำให้เศรษฐกิจอ่อนแอ
ปัญหาอย่างหนึ่ง คือ การที่ปศุสัตว์ของกูชถูกปล่อยให้กินหญ้ามากเกินไป เมื่อโคนมกินหญ้าหมด ลมก็พัดพาดินออกไป
ทำให้เกษตรกรผลิตอาหารได้น้อยลง
อีกอย่างหนึ่ง
ช่างเหล็กใช้ป่าไม้ใกล้เมืองมีโรจนหมดสิ้น ในขณะที่ไม้กลายเป็นสิ่งที่ขาดแคลน
เตาหลอมก็ถูกปิดลง กูชผลิตอาวุธและขายสินค้าได้น้อยลง
กูชยังมีความอ่อนแอจากการขาดทุนด้านการค้าขาย
พ่อค้าต่างแดนได้จัดตั้งเส้นทางการค้าขายใหม่ไปรอบ ๆ กูช เส้นทางการค้าขายดังกล่าวเส้นหนึ่งผ่านกูช
ไปสู่ทางที่ดีกว่า คือ อักซุม (Aksum) ซึ่งเป็นอาณาจักรที่ตั้งอยู่ตามฝั่งทะเลแดงซึ่งปัจจุบันคือ
ประเทศเอธิโอเปียและเอริเทรีย (Ethiopia and Eritrea) ในสองคริสต์ศตวรรษแรก
อักซุมเจริญมั่งคั่งจากการค้าขาย
ประมาณคริสต์ศตวรรษที่
300 กูชสูญเสียความมั่งคั่งและความสามารถทางทหารมากมาย กษัตริย์แห่งอักซุมจึงได้เปรียบจากความอ่อนแอของคู่แข่งทางด้านการค้าขายในยุคต่อมา
เมื่อประมาณคริสต์ศตวรรษที่ 350 กองทัพอักซุมของกษัตริย์ เอซานา (King Ezana) ก็ได้ทำลายเมืองมีโรและปกครองกูช
ในปลายศตวรรษที่
300 ผู้ปกครองอักซุมกลายคริสเตียน ประมาณสองร้อยปีต่อมา
ชาวนูเบียหลายคนก็เปลี่ยนศาสนาด้วย อิทธิพลของกูชยุคสุดท้ายจึงสูญสิ้นไป
|
Piankhi
c. 751–716 BC
Also known as Piye, Piankhi was
among Kush’s most successful military leaders. A fierce warrior on the battlefield, the king was also
deeply religious. Piankhi’s belief
that he had the support of the gods fueled his passion for war against Egypt. His courage inspired his troops on the battlefield. Piankhi loved his horses and was buried with eight of his
best steeds.
|
พิอังค์อิ (Piankhi – มีชีวิตระหว่าง 751 – 716 ปี
ก่อนคริสตกาล)
พิอังค์อิ
เรียกว่าอย่างหนึ่งว่า ปิเย เป็นผู้นำทางทหารผู้ประสบผลสำเร็จมากที่สุดของกูช
นักรบผู้ดุร้ายคนหนึ่งในสนามรบ เป็นกษัตริย์ผู้มีความเลื่อมใสทางศาสนาอย่างลึกซึ้ง
ความเชื่อของเปียงคีที่ว่า พระองค์เป็นผู้ช่วยเหลือเทพเจ้าทั้งหลาย
ได้เติมเชื้อเพลิงความกระตือรื้อร้นในการทำสงครามกับอียิปต์ ความกล้าหาญของพระองค์เป็นแรงบันดาลใจให้กองทัพของพระองค์ในสนามรบ
เปียงคีรักม้าของพระองค์และได้รับการฝังพระศพกับม้าชั้นเยี่ยมที่สุดของพระองค์
จำนวน 8 ตัว
|